Diabetes is often a silent killer, but your body gives early warning signs. Learn the 6 key symptoms of diabetes that could indicate a serious health risk and how timely diagnosis can prevent heart disease, kidney damage, and more.
6 Warning Signs of Diabetes You Shouldn’t Ignore
Diabetes is often referred to as a “silent disease” because it may go unnoticed for years, silently damaging your organs until it reaches a critical point. By the time many people realize they have diabetes, serious complications like heart disease, kidney damage, and vision loss may already be in motion.
However, your body frequently gives out early warning signs. Recognizing these symptoms early on can significantly reduce the risk of long-term damage, especially to vital organs like the heart and kidneys. Dr. Anil Mishra, Consultant Cardiologist at BM Birla Heart Hospital, shares the six most common red flags that could indicate diabetes and require immediate attention.
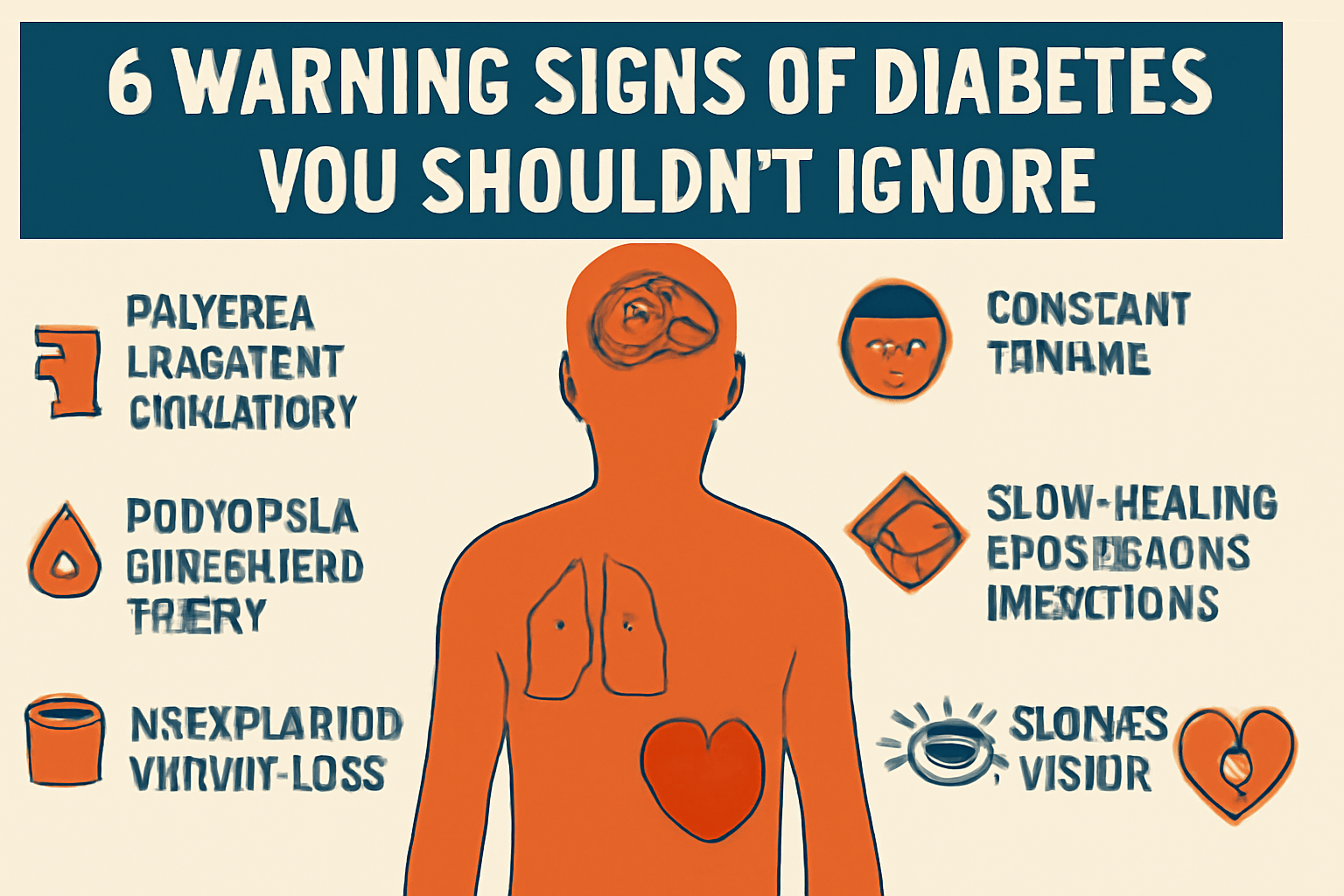
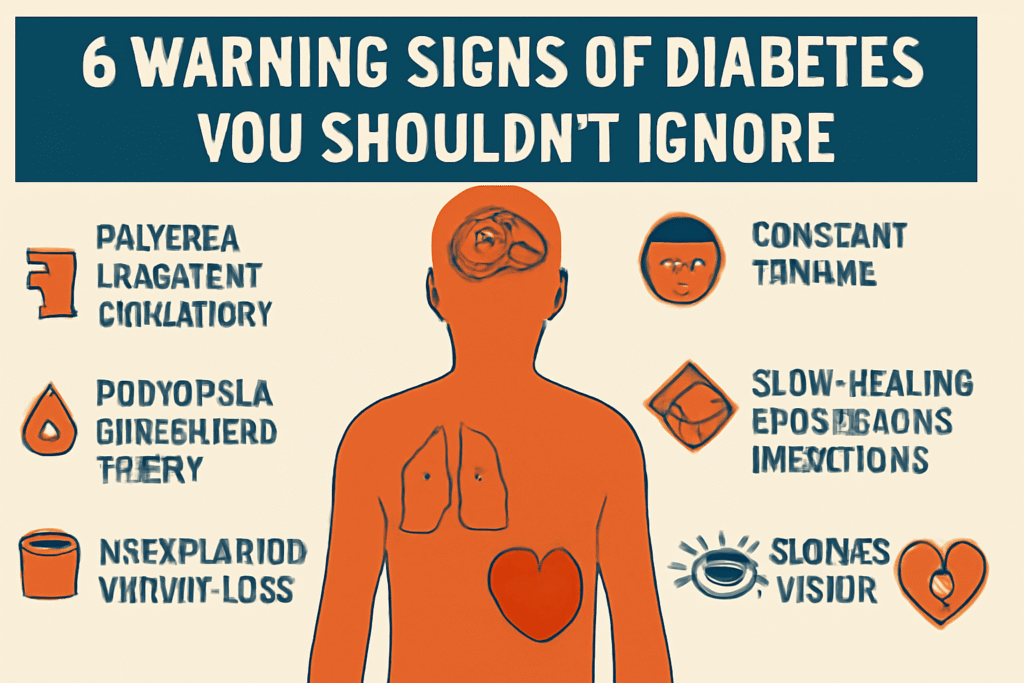
1. Polyuria (Frequent Urination)
Do you often feel the urge to urinate, especially during the night? This could be one of the first signs of diabetes. High blood glucose levels force the kidneys to work harder, filtering out excess glucose and leading to frequent trips to the bathroom.
2. Polydipsia (Increased Thirst)
Excessive thirst that doesn’t seem to be quenched no matter how much you drink may indicate high blood sugar. As glucose is lost through frequent urination, your body becomes dehydrated, prompting an unrelenting thirst.
3. Unexplained Weight Loss
Unexpected weight loss can be a troubling sign. Even when food intake remains the same, the body may begin to break down muscle and fat for energy when it can’t properly use glucose, resulting in unintentional weight loss.
4. Constant Fatigue
Feeling exhausted and drained despite adequate rest could be linked to diabetes. When glucose isn’t converted into energy efficiently, it leaves individuals feeling fatigued and weak throughout the day.
5. Slow-Healing Wounds and Infections
If you notice that cuts and wounds are taking longer to heal than usual, it could be a sign of diabetes. High blood sugar levels damage blood vessels, reducing circulation and making it harder for wounds to heal properly.
6. Blurry Vision
High blood sugar levels can cause swelling in the lenses of your eyes, leading to temporary blurry vision. If left unchecked, it can lead to more severe eye problems, including irreversible damage and even blindness.
Effects of Diabetes on Heart Health
Diabetes doesn’t just affect blood sugar levels; it also significantly increases the risk of cardiovascular diseases. In fact, nearly 65% of people with diabetes develop heart disease over time. Here’s how it happens:
- Increased Hypertension Risk: Approximately 50% of diabetics experience high blood pressure, a leading cause of heart disease.
- Elevated “Bad” Cholesterol (LDL) and Triglycerides: High levels of these fats in the blood contribute to artery plaque buildup, narrowing the arteries and increasing the risk of heart attacks and strokes.
- Obesity: Obesity, common among diabetics, further stresses the heart and leads to complications.
- Premature Heart Disease: Heart disease can develop ten years earlier in people with diabetes, often with severe arterial damage.
- Higher Complication Rates: Diabetic individuals develop artery blockages faster, leading to higher risks during heart surgery and angioplasties.
Prevention and Control
Regular blood glucose monitoring is crucial for managing diabetes and minimizing the risks associated with heart disease. A balanced, healthy diet, combined with regular exercise, is essential in maintaining a healthy weight and keeping blood sugar levels in check.